4 Stroke Engine Diagram and Working Principle
Four-stroke-engine is the commonly uses type of engine that many cars have. There are reason why many cars use 4-stroke-engine, basically four stroke engine has lower fuel consumption.
That’s make cars more economic, moreover this type of engine has better emission than two stroke engine.
Today, we’ll learn about the diagram of 4 stroke engine cycle. If you have a question, how four stroke engine work ? in this article you will find the answer.
As the name, this engine have 4 steps in a cycle.
Before we discuss about working principle, you need to understand main part of this engine. At least, there are 4 main part ;
After you understand the main part, lets discuss the main menu ;
1. Intake stroke

Intake stroke is a process where gas (a mixture of air and fuel with a certain level) are inserted into a room inside the engine, this room called a combustion chamber.
The way it works, it starts from the piston whose position is on the TDC (top dead center). This position means, the piston position is at the top in the cylinder block. This position, will leave very little space in the combustion chamber.
However, when the intake stroke start when the piston move down. So that the combustion chamber volume will increase, and the impact of the vacuum in the combustion chamber is also getting bigger. Enlargement of the combustion chamber volume due to the piston movement downwards, in another side intake valve open and it will suck up the gas that has been prepared to enter the enlarged combustion chamber.
Where can gas enter the combustion chamber?
Which should not be forgotten, the 4 stroke engine has a valve mechanism that can regulate valve openning according to timing (when the suction step is in). In this case, when the intake stroke start, the intake valve will open so that the gas from the intake manifold can enter smoothly into the combustion chamber.
At the end of the suction step, the piston position is at the BDC (bottom dead center) ie the position where the piston is located at the lower end of the cylinder block. Its make the volume of combustion chamber is at maximum volume and is fully charged with gas ready to be burned.
2. Compression stroke

The compression stroke is a process to increase the pressure and temperature of the gas inside of combustion chamber, that’s because to get higher explosive power or expansion, we need to burn gas on the higher temperature and volume.
Maybe you've seen an explosive firecracker. Why can firecrackers explode? and is there expansion power too? That's because there are explosive powders burned in a closed room. Even on a machine, the engine does not use explosive powder but uses gas.
Typically this gas is easy to adjust space and flammable but its expansion power is low. To increase the expansion power, one of the methods used is to increase the pressure and temperature of the gas.
The compression stroke starts when the piston in the BDC position moves to the TDC (moves up). Previously at the end of the suction step, the combustion chamber at the maximum volume was filled with gas. While on rare compression, the piston moves back upward. In other words this movement will decreases the volume of combustion chamber.
In this condition, the intake valve and exhaust valve are tightly closed. So that the compression inside combustion chamber volume will compress the gas in the combustion chamber. Until the end of the compression step, the gas pressure and temperature are already at their highest level so they are ready to be burned.
3. Power stroke/combustion stroke

Combustion steps can be interpreted as playing a stroke, because in this step the combustion occurs. Previously at the end of the compression step, the piston position was already above with the gas in the combustion chamber in full pressure and high temperature.
Under these conditions, litle triggers (such as electric sparks) can burn gas. So that when this stroke takes place, the spark plug will sprinkle the fire. As a result, high pressure gases burn and cause considerable explosive power.
But the construction of the engine has been made in such a way as to withstand the power of expansion. So that the explosive power of the combustion can be directed to re-move the piston downward. The power of expansion, will influence the piston movement power. At the end, the power of piston movement will influence the vehicle power.
In other words, why can the piston move up and down itself in the engine? it is due to the influence of the impulse or explosive power during combustion. The expansion power has enough power so that not only can the piston move up and down but can also move the car's powertrain until the car can go fast.
4. Exhaust stroke
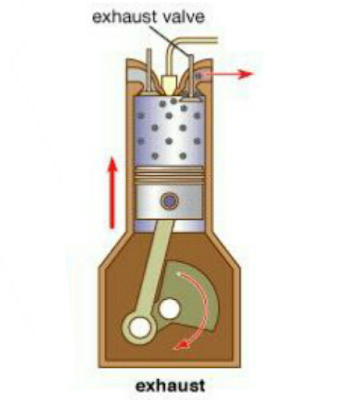
This is the last step of the 4 stroke engine cycle, at this step there is a discharge of combustion residual gas from the combustion chamber to the exhaust.
The process takes place when the piston receives expansion power, the piston moves to the BDC. When the piston arrive BDC, the piston moves directly upward due to the crankshaft mechanism. When the piston moves to this TDC, the exhaust valve opens. So that the piston directly pushes the combustion residual gas to exit through the exhaust manifold pipe.
Then, when the piston reaches the TDC the exhaust valve will be closed and return to the suction step to continue the next engine cycle.
Maybe enough for now, hope you understand this discussion hope this usefull for all of you.
That’s make cars more economic, moreover this type of engine has better emission than two stroke engine.
Today, we’ll learn about the diagram of 4 stroke engine cycle. If you have a question, how four stroke engine work ? in this article you will find the answer.
4 Stroke Engine Working Principle
As the name, this engine have 4 steps in a cycle.
- Suction/intake stroke
- Compression stroke
- Combustion stroke
- Exhaust stroke
Before we discuss about working principle, you need to understand main part of this engine. At least, there are 4 main part ;
- Cylinder block, tubular part that uses for piston movement.
- Head cylinder, closed top cylinder that use as combustion chamber and the housing part of another engine part (ie : spark plug, and valve mechanism).
- Piston, silindrical part that move upwad and downward. The movement of piston will change the volume inside the combustion chamber, that’s the main idea of 4 stroke engine working.
- Valve mechanism, this valve have a role as door to enter the air inside the combustion chamber and to take out exhaust gases to the mufler. The valve, operated by a mechanism that bound to the crank shaft of engine.
After you understand the main part, lets discuss the main menu ;
1. Intake stroke

Intake stroke is a process where gas (a mixture of air and fuel with a certain level) are inserted into a room inside the engine, this room called a combustion chamber.
The way it works, it starts from the piston whose position is on the TDC (top dead center). This position means, the piston position is at the top in the cylinder block. This position, will leave very little space in the combustion chamber.
However, when the intake stroke start when the piston move down. So that the combustion chamber volume will increase, and the impact of the vacuum in the combustion chamber is also getting bigger. Enlargement of the combustion chamber volume due to the piston movement downwards, in another side intake valve open and it will suck up the gas that has been prepared to enter the enlarged combustion chamber.
Where can gas enter the combustion chamber?
Which should not be forgotten, the 4 stroke engine has a valve mechanism that can regulate valve openning according to timing (when the suction step is in). In this case, when the intake stroke start, the intake valve will open so that the gas from the intake manifold can enter smoothly into the combustion chamber.
At the end of the suction step, the piston position is at the BDC (bottom dead center) ie the position where the piston is located at the lower end of the cylinder block. Its make the volume of combustion chamber is at maximum volume and is fully charged with gas ready to be burned.
2. Compression stroke

The compression stroke is a process to increase the pressure and temperature of the gas inside of combustion chamber, that’s because to get higher explosive power or expansion, we need to burn gas on the higher temperature and volume.
Maybe you've seen an explosive firecracker. Why can firecrackers explode? and is there expansion power too? That's because there are explosive powders burned in a closed room. Even on a machine, the engine does not use explosive powder but uses gas.
Typically this gas is easy to adjust space and flammable but its expansion power is low. To increase the expansion power, one of the methods used is to increase the pressure and temperature of the gas.
The compression stroke starts when the piston in the BDC position moves to the TDC (moves up). Previously at the end of the suction step, the combustion chamber at the maximum volume was filled with gas. While on rare compression, the piston moves back upward. In other words this movement will decreases the volume of combustion chamber.
In this condition, the intake valve and exhaust valve are tightly closed. So that the compression inside combustion chamber volume will compress the gas in the combustion chamber. Until the end of the compression step, the gas pressure and temperature are already at their highest level so they are ready to be burned.
3. Power stroke/combustion stroke

Combustion steps can be interpreted as playing a stroke, because in this step the combustion occurs. Previously at the end of the compression step, the piston position was already above with the gas in the combustion chamber in full pressure and high temperature.
Under these conditions, litle triggers (such as electric sparks) can burn gas. So that when this stroke takes place, the spark plug will sprinkle the fire. As a result, high pressure gases burn and cause considerable explosive power.
But the construction of the engine has been made in such a way as to withstand the power of expansion. So that the explosive power of the combustion can be directed to re-move the piston downward. The power of expansion, will influence the piston movement power. At the end, the power of piston movement will influence the vehicle power.
In other words, why can the piston move up and down itself in the engine? it is due to the influence of the impulse or explosive power during combustion. The expansion power has enough power so that not only can the piston move up and down but can also move the car's powertrain until the car can go fast.
4. Exhaust stroke

This is the last step of the 4 stroke engine cycle, at this step there is a discharge of combustion residual gas from the combustion chamber to the exhaust.
The process takes place when the piston receives expansion power, the piston moves to the BDC. When the piston arrive BDC, the piston moves directly upward due to the crankshaft mechanism. When the piston moves to this TDC, the exhaust valve opens. So that the piston directly pushes the combustion residual gas to exit through the exhaust manifold pipe.
Then, when the piston reaches the TDC the exhaust valve will be closed and return to the suction step to continue the next engine cycle.
Maybe enough for now, hope you understand this discussion hope this usefull for all of you.


